The U.S. Patent and Trademark Office on Tuesday granted Apple's invention for an earphone cable capable of detecting when its being shared between multiple users, allowing each to hear a monophonic audio track or completely different songs.
Source: USPTO
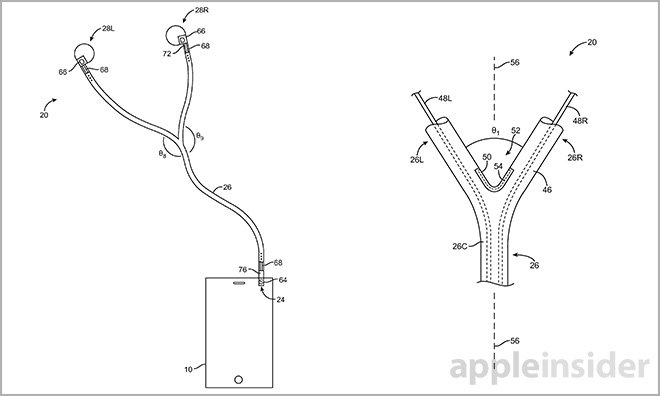
Apple's U.S. Patent No. 9,049,508 for "Earphones with cable orientation sensors" employs a variety of sensors to determine the presence of one or more users and subsequently output audio in single- or multi-user mode. For example, a stereo sound scheme may be employed when a single user is detected, while multiple users get separate mono signals.
A number of viable sensor arrangements are disclosed involving mechanical switches, strain gauges, capacitive sensors and even light transmission via fiber optics. Depending on an earphone's design, sensing modules are disposed at specific points along an earphone's cable, such as the Y-junction that joins left and right channel wires.
Some embodiments, like those dealing with Y-junction installations, rely on angle measurements to determine when an earphone is being shared by multiple users. The invention assumes the angle will change when two users share earphones, likely widening the gap between left and right earbuds compared to a single-user scenario.
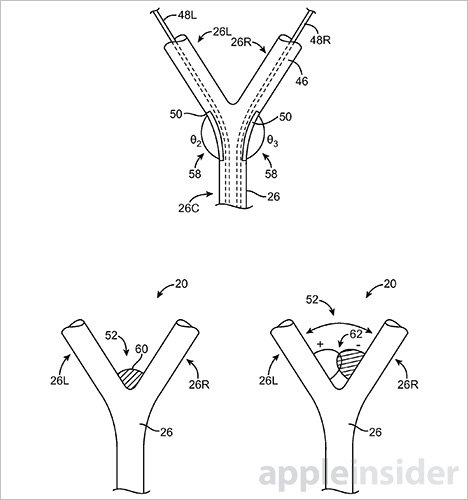
This technique incorporates sensors within a cable's rubber sheath either as conductive lines or integrated with an internal support structure. Strain gauges and conductive lines can be located at the Y-junction to measures minute changes in angle between exiting left and right cable sections. When a measured angle surpasses a predetermined threshold, it is concluded that multiple users are sharing the device, which in turn triggers a specific audio profile.
Another technique involves capacitive sensors, applied as overlapping conductors again placed at the Y-junction. When left and right cable segments are spread apart the overlapping area decreases, thereby decreasing capacitance, a change that can be continuously monitored.
One embodiment uses a fiber optic goniometer, a device capable of measuring precise angles using known properties of light transmission. Light from a laser, LED or other source is polarized, piped through fiber optic cabling and multiple wave plates, then collected at detectors placed in both earbuds.
As light passes through the fiber optic cable, changes in polarization occur when one wave plate rotates in respect to other wave plates, which in turn modulates light intensity as captured by the light detector. The resulting data is processed and translated as a specific cable position.
Apple's patent also outlines other sensor techniques, including piezo-electric force sensors, as well as equations for assigning appropriate thresholds to single- and multi-user scenarios.
Today's IP grant is unlikely to show up in a near-future EarPods product, but a form of the design could come in handy for other solutions involving data and power cable management. Apple has shown increased interest in minimizing customer reliance on cords, as evidenced by the Apple Watch's inductive charger and the new 12-inch MacBook's single USB Type-C cable, which could lead to compatibility issues as device designs adapt.
Apple's earphone cable orientation sensor patent was first filed for in 2012 and credits Paul G. Puskarich as its inventor.