Google is starting to roll out access to Google Bard, its AI chatbot competitor to ChatGPT that aims to use machine smarts to provide intelligent responses to queries.
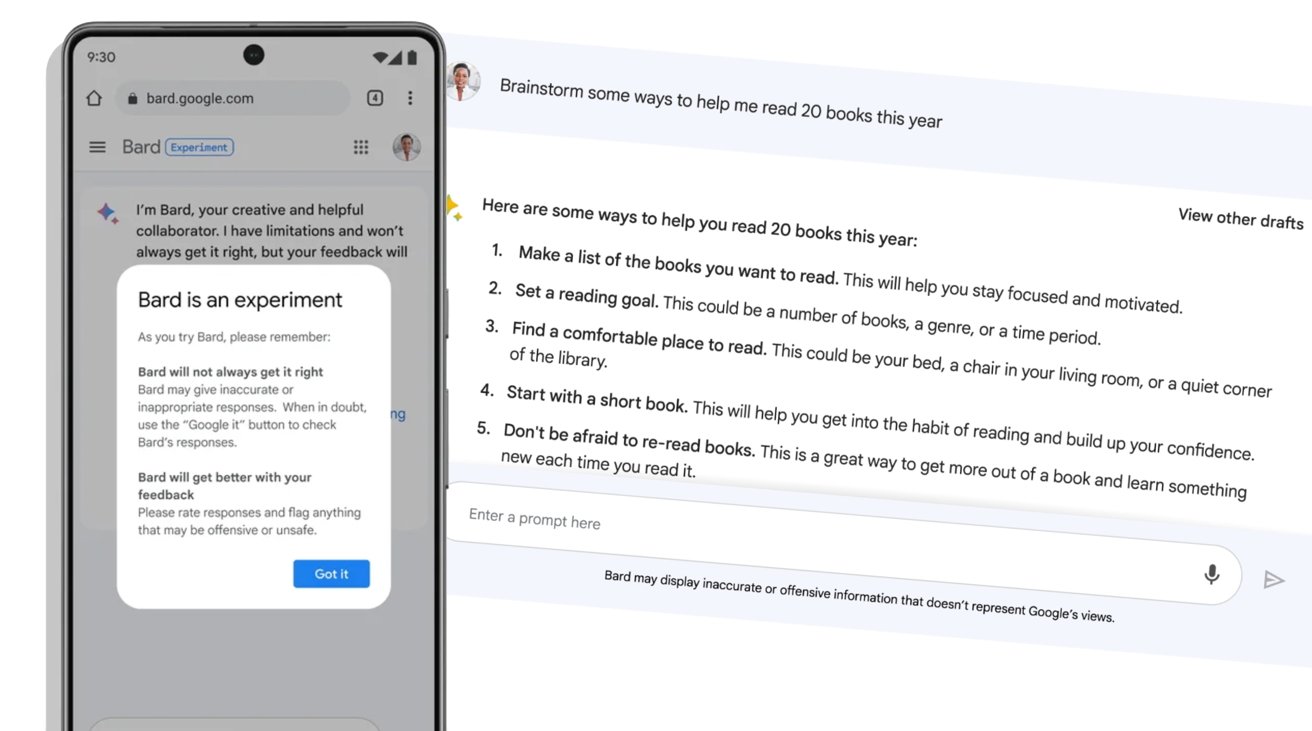
Google Bard is rolling out to users.
First introduced in February, Google Bard was billed as an experimental conversational AI service that offers direct access to queries instead of just search results. After initial testing using "trusted testers," the search giant is finally allowing the general public to try it all out.
Starting from Tuesday, Google is accepting sign-ups for the waitlist to use Bard. Initially open in the United States and the UK, Google says it will expand access to more countries and languages over time.
Google Bard is powered by a research large language model consisting of a lightweight version of LaMDA (Language Model for Dialogue Applications) that reads and parses queries from the user. It then, one word at a time, selects the next word in the sentence from a list that is likely to come next.
This decision is based on the probability of words that could be predicted to be used next in a statement, based on the prompt, what it had already generated, and its vast knowledge base.
In a lengthy blog post about the initiative, Google acknowledges the possibility of getting things wrong, with due to LLMs learning "from a wide range of information that reflects real-world biases and stereotypes." This can lead to LLMs providing "inaccurate, misleading or false information while presenting it confidently."
While this was demonstrated during an initial demo, Google's latest example shows a failure in identifying the scientific name for a plant.
To counter the inaccuracy issue, users may be given multiple draft responses so the user can pick the best. Users can then continue from a draft by asking follow-up questions, and again potentially see alternate answers.
Continuing the theme of avoiding issues of other platforms, Bard is being guided by Google's "AI Principles," with assurances of a focus on quality and safety. This includes using human feedback and evaluation, and guardrails such as "capping the number of exchanges in a dialogue."
Google's introduction of Bard is a response to Microsoft's tie-up with ChatGPT, which as resulted in the creation of a chatbot for Bing. AppleInsider found Bing's version to be both good but also lacking, which further iterations will improve upon.
