A pair of Apple patent applications published Thursday indicate research into alternative input methods for iOS, namely a touch sensitive stylus and a device capable of customizing a user interface based on whether a user is holding it in their left or right hand.
Apple's application for a "Stylus with touch sensor," as published by the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office, describes a next-generation input device that incorporates an array of capacitive touch sensors along its body to determine the position of a user's fingers. Information gathered by these sensors can be interpreted as gestures for onscreen UI control.
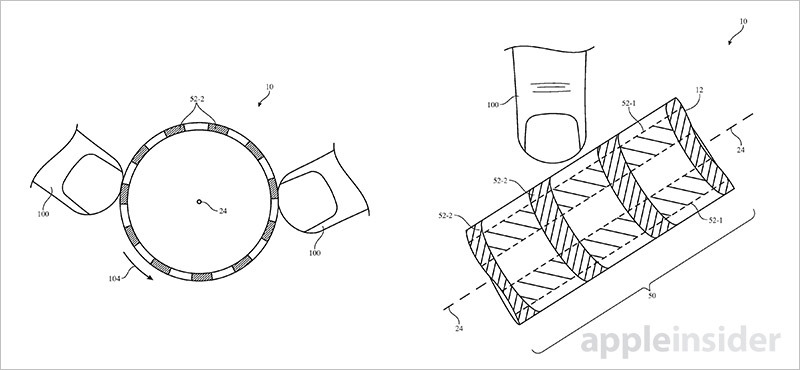
In some embodiments electrodes might be installed in both longitudinal and circumferential arrangements — wrapped around the body — to facilitate accurate detection of multiple concurrent touch events, or contact with multiple fingers. The system is able to process both single- and multi-touch gestures, which can then be used to manipulate onscreen objects.
Fine finger location determination opens the door to advanced device interactions. For example, Apple notes its sensor design can detect that a user is rotating the stylus based on positioning data from two or more fingers. This information might then be applied to rotate an onscreen object, select brush size in a drawing app or control any number of system UI parameters.
Stylus touch data also includes motion gestures. For example, running a single finger up or down the stylus body might invoke a scrolling operation, while a flicking motion initiates an inertial scroll.
Apple also includes a contingency for force sensors which can be used in concert with stylus touch sensors to invoke special UI adjustments. For example, a user may increase drawing precision by gripping the stylus tightly, or toggle virtual buttons with a squeeze. If the stylus is equipped with an accelerometer, a pinch gesture might also be used to "pick up" and move onscreen objects.
As usual, whether Apple plans to implement the invention in a shipping product like Apple Pencil unclear.
Apple's touch sensitive stylus patent application was first filed for in December 2014 and credits Ray L. Chang as its inventor.
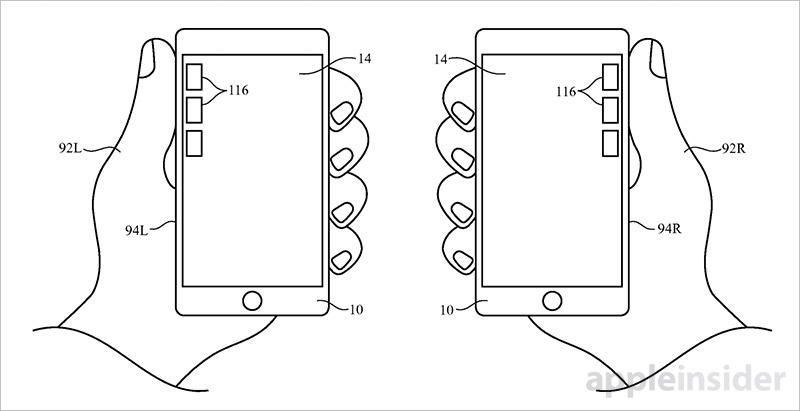
A second application for "Electronic devices with hand detection circuitry" describes a method of employing specialized sensors to determine whether a user's left or right hand is being used to operate a device, then customize the system UI for one-handed use. The invention could come in handy for a great number of iPhone 6 and 6s owners who find it difficult to wield enlarged handsets with one hand.
For example, icons, virtual buttons and other onscreen controls might shift to the right side of a device screen if it is determined that a user is holding the phone in their right hand. The process can be reversed for a left-handed user.
For the system to be effective, and not a nuisance to the end user, determination must be quick and accurate. Apple says dedicated dominant hand sensor circuitry such as specialized touch sensors can be employed for the task, but notes iPhone's included sensor suite is sufficient.
In some embodiments, Apple's system relies on motion sensors to detect device rotation and movement, both parameters that might inform how a handset is being held. Proximity sensors embedded in the walls of an iPhone chassis might also be useful. Fingerprint sensor data is an obvious choice, as technologies like Touch ID are capable not only of associating a given fingerprint image with a user's left or right hand, but also determining its orientation.
Alternative techniques include monitoring device orientation and motion during normal operation, tracking radio antenna performance and following the arc of a user's thumb as it navigates the device display, among others.
It is unclear if Apple intends to include the invention in a future version of iOS, though the company has in the past investigated solutions for single fisting large-format handsets. When the iPhone 6 and 6 Plus debuted with 4.7-inch and 5.5-inch screens, respectively, Apple introduced an iOS feature called Reachability. Still available on iPhone 6s and 6s Plus, the function allows users to double tap — not press — on the home button to drop all onscreen content down to the lower half of the screen, thus bringing it within thumb's reach.
Apple's ambidextrous Reachability application was first filed for in December 2014 and credits Thayne M. Miller as its inventor.
 Mikey Campbell
Mikey Campbell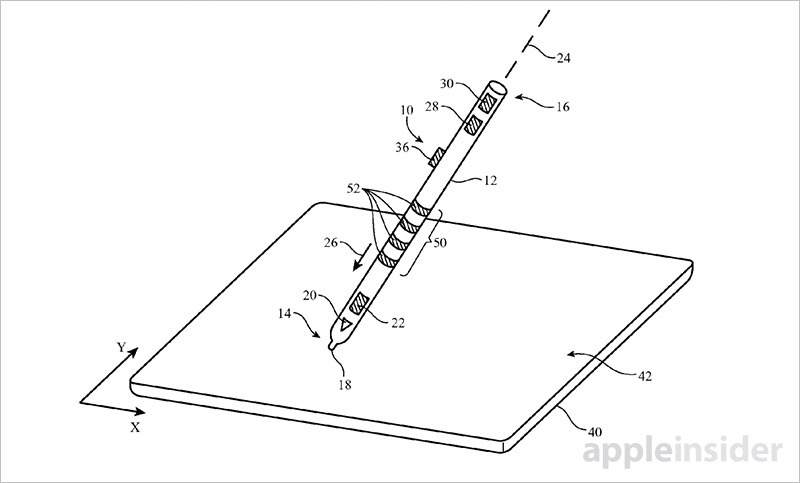



-xl-m.jpg)


-m.jpg)






 Chip Loder
Chip Loder
 Thomas Sibilly
Thomas Sibilly
 Wesley Hilliard
Wesley Hilliard
 Christine McKee
Christine McKee
 Amber Neely
Amber Neely
 William Gallagher
William Gallagher
 Malcolm Owen
Malcolm Owen







14 Comments
Yeah, but, Apple doesn't innovate. /s
"Apple invents..." is less accurate than "Apple patents". Frankly, the left-handed UI is an obvious design that should already exist. I was thinking about this a couple days ago (most specifically when using my phone left-handed and finding it works far less well, especially left-handed thumb typing). Silly me, I didn't patent it first. Then again, there are plenty duplicate patents already...
They didn't patent left-handed design... they patented the idea of position sensors on a handheld device that could determine which hand you were holding it in with the notion that it could alter the user interface accordingly. The novelty is in it's ability to detect the hand being used without you telling it.
Seems to me the stylus detection and UI adjustment for right- versus left-handed use is clearly innovation. I mean, this isn't something that would even have been an issue in the era of Wytec and other stylus tablet input, as those were non-display tablets (different meaning of tablet versus how we use the term today) and so there wasn't an interface to interact with in the same sense there is today. I must admit, I was blown away a couple days ago reading about the 'massive innovation' that Twitter adding some video capabilities was described as, and yet these fundamental innovations brought to the world by Apple are scoffed at.