Apple last week posted a new support document to its website detailing a few tips designed to help customers distinguish official emails from phishing attempts, the latter of which have become increasingly sophisticated in recent months.
In a new document, appropriately titled "Identify legitimate emails from the App Store or iTunes Store," Apple explains scammers and other nefarious actors might use the company's name, logo and other credentials to trick users into handing over sensitive data.
As the company explains, phishing emails often resemble official Apple correspondence, with similar formatting, language and graphics. Often included are links to what appear to be legitimate Apple websites, but the pages are merely fences designed to gather personal details like a home address or credit card information.
Many phishing emails come in the form of phony App Store, iTunes Store, iBook Store or Apple Music receipts. The goal is to fool a target into thinking they were erroneously billed. Victims are often instructed to correct the mistake by following a malicious link to update account information or provide the same to a fraudulent email address.
To assist customers in identifying real Apple email from fake phishing schemes, the company says genuine purchase receipts include a current billing address, information scammers are unlikely to have. If a user wants to check on a particular charge, they can review their purchase history by navigating to Settings > [your name] > iTunes & App Store on iOS or Account > View My Account in iTunes.
Further, Apple never asks for social security numbers, maiden names, full credit card numbers or credit card CCV codes in emails about App Store, iTunes Store, iBooks Store or Apple Music purchases.
When an email requests an update to account or payment information, Apple suggests doing so only through controlled avenues like the Settings app on iPhone or iTunes on a Mac or PC. The same goes for updating an Apple ID password, an action that should be accomplished in the Settings app or through http://appleid.apple.com/.
Apple is always on the lookout for phishing emails, and urges users who have received such correspondence to forward it to reportphishing@apple.com.
Finally, for users who think they might have handed over personal information like a password or credit card information to a phony website, Apple says the best course of action is to reset their Apple ID password.
The recently published support document joins a similar help page, "Avoid phishing emails, fake virus alerts, phony support calls, and other scams," that was last updated in November.
 Mikey Campbell
Mikey Campbell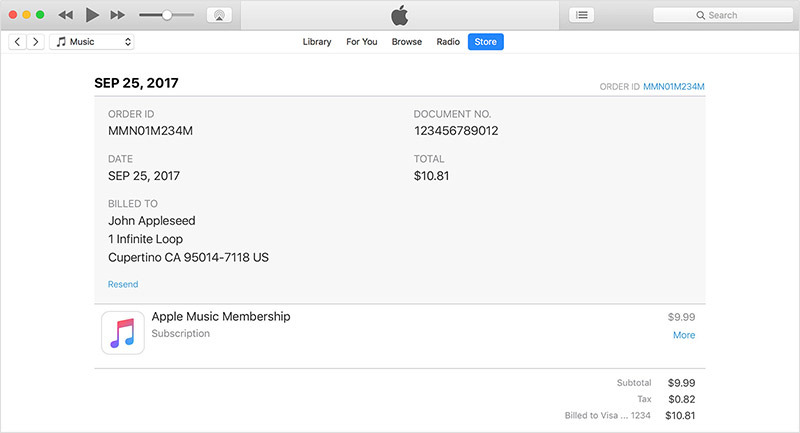







-m.jpg)






 Christine McKee
Christine McKee
 Marko Zivkovic
Marko Zivkovic
 Mike Wuerthele
Mike Wuerthele

 Amber Neely
Amber Neely
 Sponsored Content
Sponsored Content
 Wesley Hilliard
Wesley Hilliard









23 Comments
SSN’s have been made obsolete by the digital age...
I wonder when they’ll start using cryptographic keys.
Only use the iTunes interface on Mac or PC or the Settings app on iPhone,iPad or iPod Touch to update Apple ID information.
Also , use a VPN on public WiFi.Or better yet use LTE or 3G.
When my iPhone X got stolen in Spain, I started getting texts and eventually emails pretending to be "found iPhone" reports and links to fake Apple sign-in pages to try and get my Apple ID and unlock the phone. I'm smart enough to know the difference, but I bet this works often — especially because they initially were texting my friend who was still texting me around the time the theft occurred, and later my two Emergency ID contacts. So I can imagine someone's contact getting the text, then telling the owner of the phone "Hey Apple is getting ahold of me and needs your Apple ID and password to get your phone back!" etc.
The last email I got I traced to a domain registered in Barcelona (where it was stolen) and linked to a website with a domain registered in Russia. Decided it wasn't worth the trouble reporting any of this as they send from random SIMs and domains all the time. Most of the domains look loosely like iCloud such as lcoud.pw etc.
I've gotten tired of sending them pictures of my middle finger in response, so haven't been responding lately. Hope they enjoy their $1150 paperweight.
I have to say that I came close to getting scammed a couple of times. Both times when I was traveling abroad.