Apple's patch on Tuesday seems to fix most — if not all — of the clock speed excursions that the 15-inch MacBook Pro was experiencing when under load. AppleInsider delves into the situation, runs the numbers in some real-world applications, and talks about what led us to this point.
How this began
Intel's 2.9GHz six-core Core i9 processor with Turbo Boost speeds up to 4.8GHz is offered as a premium $300 option on Apple's 2018 15-inch MacBook Pro with Touch Bar, but according to Lee, the chip is unable to reach its full potential due to the laptop's design.
In a video posted to his YouTube channel on July 17, Dave Lee shows the top-of-the-line MacBook Pro running Adobe Premiere Pro at surprisingly low clock speeds. Tests conducted by Lee put the average clock speed of the processors under load at around 2.2GHz, well below the advertised 2.9GHz.
"This i9 in this MacBook can't even maintain the base clock speed," Lee said. "Forget about Turbos and all that stuff, it can't even maintain the 2.9GHz base clock, which is absurd. This CPU is an unlocked, over-clockable chip, but all of that CPU potential is wasted inside this chassis, or more the thermal solution that's inside here."
Apple apparently worked with Lee to identify the issues, and roll out Tuesday's patch.
Benchmarks and initial testing before Tuesday's patch
Lee's test was on Adobe Premiere — a real world test, albeit one using software that performs better with an Nvidia GPU rather than an AMD one.
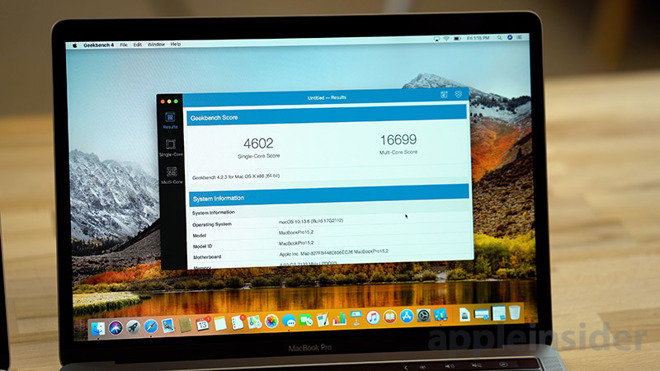
We shifted to a different benchmark for our initial series of tests. Using Cinebench 15, we ran 10 total runs on the i9 MacBook Pro.
Immediately after starting the first test, the CPU clock speed shot up to 4.17 GHz. It rapidly dropped to 3.86GHz until it hit the chip critical temperature of 100C. It then dropped nearly immediately to 2.57GHz with a temperature drop to 84C.
The speed of the processor varied between 2.33GHz and 2.9GHz during the test, with one profound dip to 2.02GHz.
The first time we ran the test, it hit 921. The second time it scored an 877, with an average across the 10 tests of 906.

We ran the same tests on the "base" i7-equipped MacBook Pro and got relatively similar results — which should not have been the case given the difference between the i7 and i9. Out of the gate, the i7 jumps to 3.8GHz, just below the advertised boosted clock rate of 4.1GHz for that chipset.
After several back-to-back tests, keeping the processors warm and the fans running, we were able to regularly get scores of up to 916. Using Intel Power Gadget, we clocked the processor speed averaging around 2.3Ghz and 2.6GHz, almost exactly what we were getting with the i9.
Both series of tests prior to Apple's patch application remained the same, when monitored with Intel's newest version of the Power Gadget CPU monitoring tool that was released over the weekend.
Post-patch
Geekbench testing was about the same as it was during the first round of testing — but that was expected.
We repeated the same Cinebench test on the MacBook Pro with Core i9 processor, under the same conditions, and the same ambient temperature. The first run of the test hit 953, with a 10-run average of 945. Clock speeds remained high, with only very brief excursions below rated speed.
A 3.5GHz speed was maintained in the Core i9 model, with most of the speed excursions only going down to 3.1GHz.
Actual projects
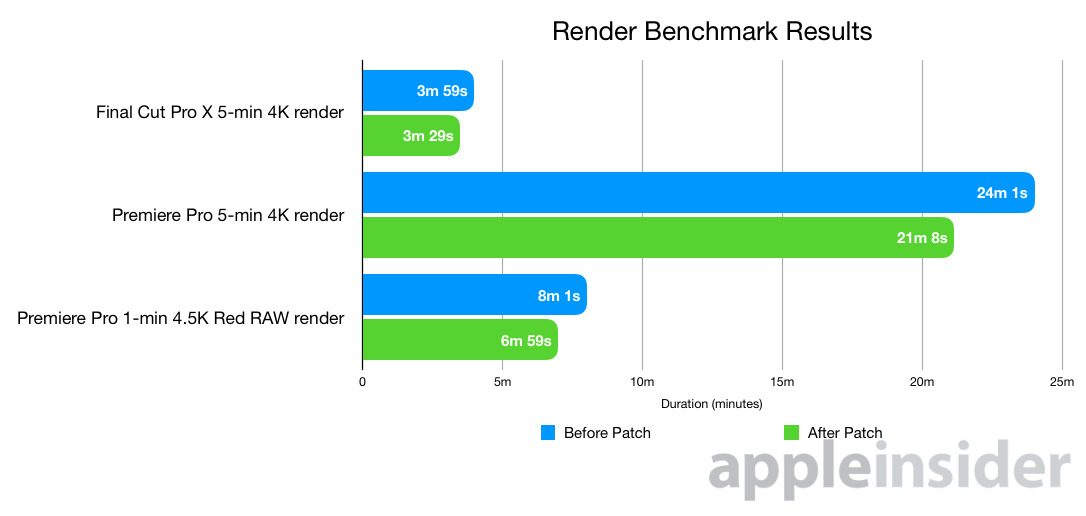
The gains aren't just measurable in a synthetic benchmark.
A five-minute 4K project with effects in Final Cut Pro X rendered in three minutes and 39 seconds before the update, and three minutes and 29 seconds afterwards.
Premiere Pro saw big gains, going from 24 minutes and one second pre-patch rendering time for the same project, to 21 minutes and eight seconds.
A one-minute 4.5K Red RAW project with effects rendered in Premiere Pro took eight minutes and one second to complete before Apple's patch, and six minutes and 59 seconds after application.
What's fixed?
We don't know yet what specifically Apple has changed. Theories, including our own, regarding the cause of the problem in the first place have varied, including voltage regulator module overheat and an insufficient thermal design.
Originally, we said that the most obvious immediate solution was for Apple alter the peak speed of the processor by adjusting the power that the CPU gets. In doing so, slowing the peak speed of the processor may have allowed it to finish tasks quicker, as it will slow down less to keep the CPU cool. But, it doesn't appear that this is what Apple has done, given the CPU speeds we saw.
Another possibility was for Apple can to alter the fan speed thresholds to accommodate a CPU load better, by setting them to kick in sooner and faster than it did at launch, but this also doesn't seem to be the case.
A third theory alleged that Intel's monitoring tool was somehow faulty, but an update to the software over the weekend didn't change the results at all. We know, because we tried the tests after the tool was re-released after a brief absence.
The patch fixes some or all of these things minutely, or is a software bug repaired elsewhere. It doesn't really matter what, though, because it appears to be fixed now.
Compared to other i9 machines on running Windows, the Cinebench testing on the i9 is still a bit behind. But, the real-world testing isn't behind by much, if at all. We'll keep looking into the situation, and run other tests moving forward.
 Mike Wuerthele
Mike Wuerthele







-m.jpg)





 William Gallagher
William Gallagher
 Sponsored Content
Sponsored Content

 Wesley Hilliard
Wesley Hilliard

 Thomas Sibilly
Thomas Sibilly

 Marko Zivkovic
Marko Zivkovic









98 Comments
It was interesting that there were significant groups out there that implied that Apple would put (on purpose) a 2.9Ghz processor into a computer that would only operate above 2.2Ghz if it was literally in a freezer, stating that clearly their engineers had not addressed thermal management, or that is was a maneuver by Apple to offer poorly integrated hardware simply to make it look like the devices were more powerful than they really were.
The digital key issue makes sense, as it would work during testing by the engineering team, but was somehow rendered invalid upon final launch of the hardware. This does seem to represent a significant quality-control issue, but nothing fatal, as it could easily be fixed by a software update issued a just few days after the computers delivered.
Did the i7 results improve post patch?
The Verge editor Dieter Bohn reached out to the company behind Cinebench (which also makes 3D modeling software Cinema 4D) to ask whether we can expect the software to accurately measure performance on this hardware. He got this response back: