The Apple Watch could offer a high level of accuracy when monitoring blood pressure, with Apple suggesting an actuator with a bladder and pressure sensors to reduce the number of errors when making a reading of the wearer.
Apple introduced blood oxygen tracking in the Apple Watch Series 6, giving users another metric in their fitness to track, alongside the heart rate and ECG features. However, one important blood-related measurement that has so far failed to be included is blood pressure monitoring.
Blood pressure monitoring would be great for people with an elevated blood pressure level, known as hypertension, as it is used as an indicator for potential health issues. Long-term and continuous monitoring of blood pressure could help identify specific patterns of hypertension, which may improve medical treatments.
While there have been rumors of a blood pressure feature being in the works, there has not been any real indication Apple is officially going down that route for a future Apple Watch model. Part of this is probably due to the extremely small size of the Apple Watch itself, and to somehow accomplish blood pressure measurements without requiring a vast amount of extra equipment, like electrodes or a blood pressure cuff.
The small size of the Apple Watch limits the sensors that could be used, which can introduce errors in readings. Furthermore, the location of the Apple Watch on the wrist isn't necessarily the best position for blood pressure readings, as there are many ligaments, bones, and other structures that could interfere with measurements, not to mention a user's own movements.
In a patent granted to Apple by the US Patent and Trademark Office on Tuesday titled "Devices and systems for correcting errors in blood pressure measurements," Apple suggests a system for an Apple Watch or another device that could perform a blood pressure measurement. The same system would also be able to handle the multitude of potential factors that could cause an incorrect reading.
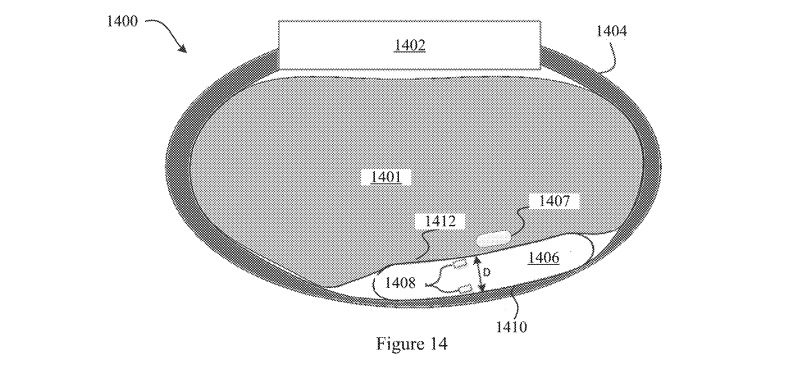
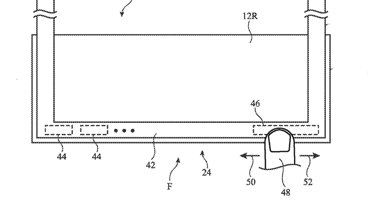
The system largely consists of a pressure sensor for measuring a pressure signal from a target artery, pressed into the wrist by an actuator. The actuator is also coupled with a further sensor to monitor the displacement of the contact end, as it moves against the wrist of the user, and is used to calculate the correct amount of pressure required to perform a reading.
A processor uses the readings to monitor for when the pressure sensor makes contact or separates from the wrist, to identify a mean arterial pressure of the target artery, and the amount of displacement as the contact end of the assembly shifts around.
As part of the patent, the processor would be configurable to estimate the tissue density based on the readings, and to factor that tissue density into the blood pressure value calculation. It is also proposed that a derivative of the pressure reading can also be produced that takes into account the movement of the sensor in relation to the wrist, as a shifting sensor will affect such a reading.
The actuator could consist of a linear actuator with the contact end potentially using a fluid or air-filled bladder to manage the position of the contact end on the wrist. The pressure sensor could be coupled to the inside or the outside of the bladder, while the actuator sensor could use optical, ultrasound, distance, magnetic, or flow-rate sensors.
 The pressure-sensing system would have to take into account wrist movements when monitoring small arteries.
The pressure-sensing system would have to take into account wrist movements when monitoring small arteries. Also, rather than being within the main body of the Apple Watch, the sensor assembly could be located at the end of a band strap, so it makes contact with the inside of the wrist. This would be a more suitable position to access arteries and veins that are needed to measure blood pressure.
Originally filed in September 2016, the patent lists its inventors as Thomas J. Sullivan, Ravi K. Narasimhan, Rui Qiao, Derek Park-Shing Young, Robert K. Montgomery II, Mohsen Mollazadeh, Zijing Zeng, Vasco D. Polyzoev, and Richard C. Kimoto.
Apple files numerous patent documents on a weekly basis, but while the existence of a filing indicates areas of interest for its research and development teams, there's no guarantee that Apple will use the concepts in a future product or service.
Patent applications from November indicate Apple is looking into ways to add a continually-monitored blood pressure feature to the Apple Watch, with the "Electrical coupling of pulse transit time (PTT) measurement system to heart for blood pressure measurement" potentially allowing it to be done without interruption to the user. A similar idea is argued in the patent application for "Blood pressure monitoring using a multi-function wrist-worn device."
In May 2020, Apple was granted a patent for "Pressure measurement designs," describing ways to perform blood pressure measurements without relying on a cuff. In that patent, Apple suggests spreading out the sensors and relying on software to calculate readings based on the wealth of resulting data.
 Malcolm Owen
Malcolm Owen



-xl-m.jpg)


-m.jpg)






 Wesley Hilliard
Wesley Hilliard
 Christine McKee
Christine McKee
 Amber Neely
Amber Neely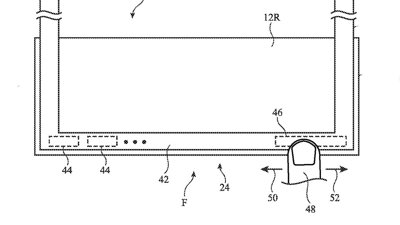
 William Gallagher
William Gallagher


 Mike Wuerthele
Mike Wuerthele







7 Comments
Optical/electrical blood glucose monitoring would be more important that blood pressure, as continuous glucose monitoring is more important than continuous blood pressure monitoring
It’s quite clear that the Apple Watch is on a path to become an indispensable tool for helping people improve their overall health and well being. Not since the iPhone has Apple released a product that has the potential to make such a profound impact on people’s lives.