Nearly one-third of the companies that Apple has added to its list of suppliers in the past three years are from mainland China, bucking talk of Apple reducing its reliance on the country.
Among the 52 new companies that Apple added to its supply chain since 2017, 15 are located in mainland China, the South China Morning Post reported Tuesday. Several of those companies are based in Shenzhen, while others are from Jiangsu.
Apple also added seven companies from the U.S. and seven companies from Taiwan to its supplier list between 2017 and 2020.
The prevalence of Chinese-based firms on the list underscores Apple's reliance on China, and the country's overall importance to the global technology supply chain during the coronavirus pandemic.
Foxconn, for example, began offering cash incentives in recent months to attract new workers amid the busy production season. In India, by contrast, Foxconn has had to cut production output by about 50% because of the COVID-19 situation there.
The number of Chinese suppliers added to Apple's shortlist also defies trade tensions between U.S. and China during the Trump administration and talks of economic decoupling amid increasing scrutiny of Chinese suppliers.
According to the South China Morning Post, the 200 companies on Apple's 2020 supplier list make up about 98% of the company's direct spend for materials, manufacturing, and assembly. About 80% of those suppliers have at least one facility in China.
Apple's reliance on China has come under scrutiny in recent years. Tech investor Peter Thiel back in April, for example, called Apple's relationship with China a "real problem." A group of U.S. lawmakers also urged Apple to exit China in May.
Apple has been accused of making a number of efforts to appease Beijing, including storing Chinese user data on locally owned servers and removing apps that run afoul of local regulations.
Additionally, there have been concerns about human rights abuses in China, specifically about allegations of companies using coerced labor. In May, a report indicated that at least seven Apple suppliers participated in labor programs suspected of oppressing minorities in China.
Follow all the details of WWDC 2021 with the comprehensive AppleInsider coverage of the whole week-long event from June 7 through June 11, including details of all the new launches and updates.
Stay on top of all Apple news right from your HomePod. Say, "Hey, Siri, play AppleInsider," and you'll get latest AppleInsider Podcast. Or ask your HomePod mini for "AppleInsider Daily" instead and you'll hear a fast update direct from our news team. And, if you're interested in Apple-centric home automation, say "Hey, Siri, play HomeKit Insider," and you'll be listening to our newest specialized podcast in moments.
 Mike Peterson
Mike Peterson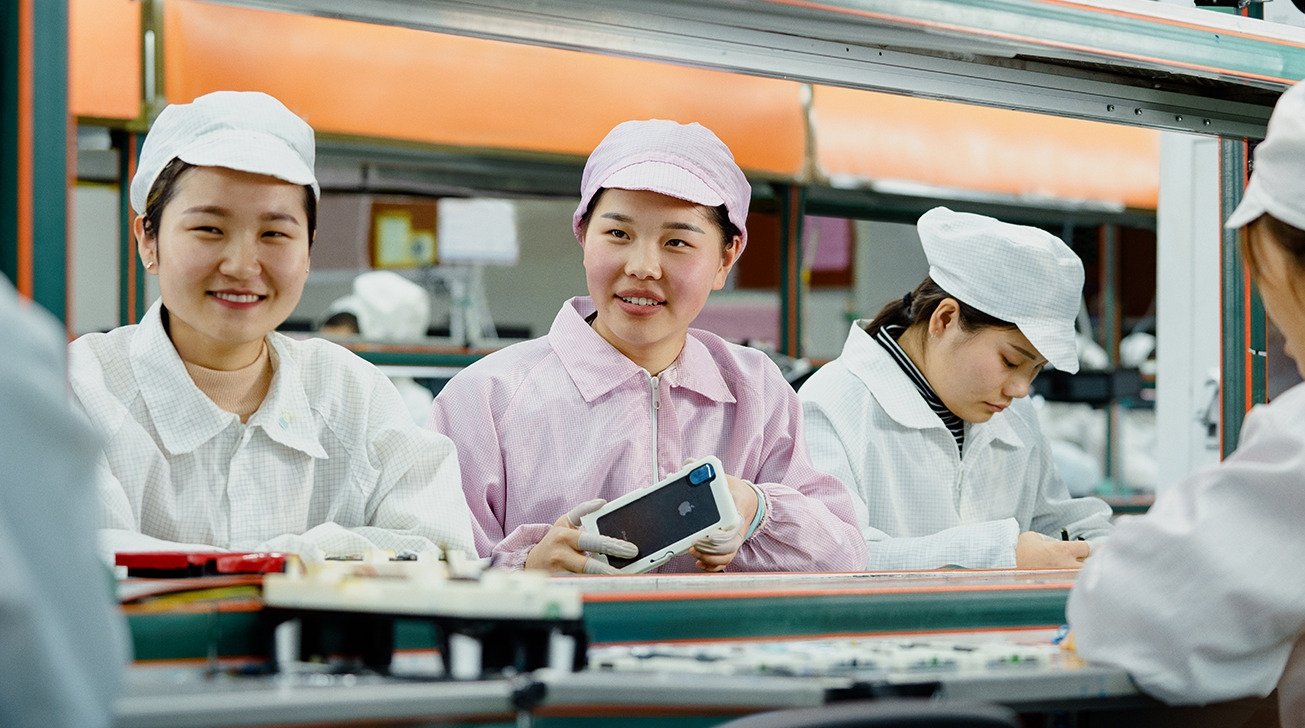







-m.jpg)






 Malcolm Owen
Malcolm Owen
 William Gallagher
William Gallagher
 Chip Loder
Chip Loder
 Brian Patterson
Brian Patterson
 Christine McKee
Christine McKee
 Wesley Hilliard
Wesley Hilliard
 Amber Neely
Amber Neely



-m.jpg)





35 Comments
The problem is that China helps our devices remain affordable. In part by keeping the development cost in line, but also by doubling Apple’s sales volume and revenue. More sales allows for lower costs overall. No one outside of China has the experience to make high tech devices at the scale required because they have the skilled labor and supply chain to support it.
It doesn’t make sense to rely too much on China. It would be better to diversify and make deals in other Asian countries like India and Vietnam
23 new companies are outside greater China and US since 2017. Where are they located? A study of them may shed some light on whether shifting supply chain out of China is feasible.