Apple has always gone for the minimalist look in anything it makes, and now new documentation suggests it wants to do away with unsightly zippers, clasps, and fasteners and use magnets instead.
Maybe the closest thing Apple will get to making clothing is the recent "Ted Lasso"merchandise, or health-monitoring gloves. But it's definitely looking at ways to make better bags and accessory cases, and the proposals work for all clothes, too.
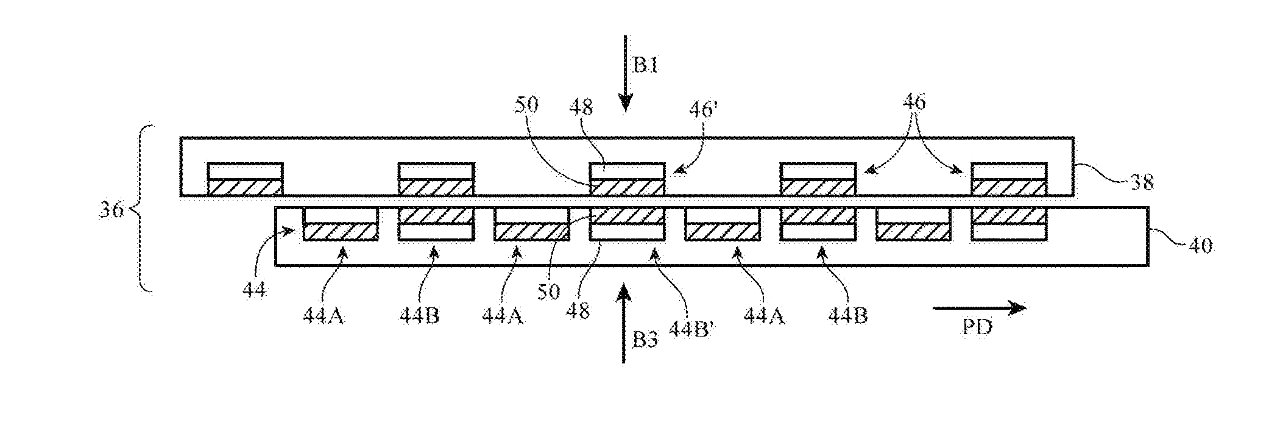
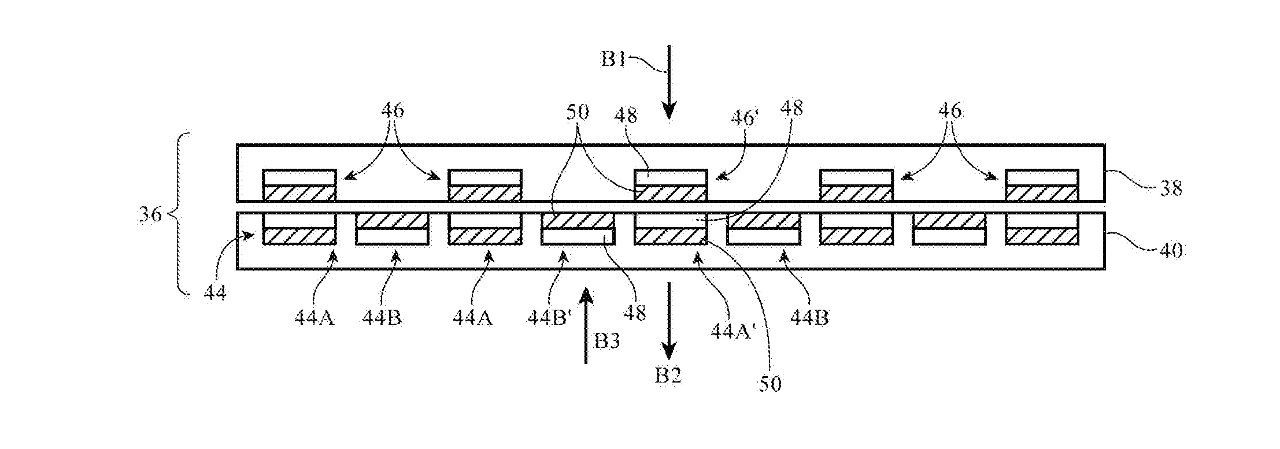
The newly-granted patent "Magnetic fastener," is concerned with replacing all zips because they are just too horrible.
"A zipper is opened and closed by moving a slider between two sets of interdigitated teeth," says the patent. "Some fasteners use magnets. For example, a magnetic clasp may be used to secure an opening in a bag. Fasteners may also be formed from snaps and buttons."
You knew that, but you may not have put a stopwatch on how fast it takes to open or close a zip. And unless you're a dressmaker trying to hide all seams, you may not be all that fussed about how a zip looks.
Apple is fussed about all of this.
"Zippers can be unsightly and may be time consuming to open and close," continues the patent. "Clasps such as magnetic clasps may be faster to open and close than zippers, but may not satisfactorily seal large openings."
Don't get Apple started on buttons. Those are sometimes "incapable of forming sufficiently tight seals for openings," and anyway are "even more time consuming to use than zippers."
Apple's proposal is to use magnets, and possibly quite a few of them.
"The magnetic fastener may have first and second portions on opposing sides of the seam," continues Apple. "When the magnetic fastener is operated in a closed state, the magnets in the first and second portions attract each other and pull the first and second portions of the fastener together to close the seam."
"When the magnetic fastener is operated in an open state," says Apple, "the magnets in the first and second portions repel each other and push the first and second portions of the fastener apart to open the seam."
In other words, magnets can securely close a seam. But you can also open that seam without too much time-consuming effort.
Maybe we'll never see an Apple cravat, or an Apple frock, with magnetic streams. Quite probably we won't see a catwalk fashion show when Apple returns to live presentations.
And some of this technology is already being used, for instance in the AirPods Max Smart Case.
Yet that specific use of magnets to make this kind of bag happens to be addressed in a separate, newly-revealed patent called "Enclosures with flexible magnetic closures and clasps."
There has never been a patent that didn't try to cover every conceivable use of its proposals. And there have been very, very many Apple patents that did not lead to particular products.
But Apple could now do clothing. It could let you say "Hey, Siri, tie my shoelaces," and have the size-adjusting laces snap shut like in "Back to the Future part II."
 William Gallagher
William Gallagher






-m.jpg)






 Christine McKee
Christine McKee
 Andrew O'Hara
Andrew O'Hara
 Marko Zivkovic
Marko Zivkovic
 Malcolm Owen
Malcolm Owen


 Sponsored Content
Sponsored Content









8 Comments
Apple loves magnets and would like to mine all the neodymium, yttrium or any other magnetic substances of the Earth
Hi freq RF exposure is another thing I LOL to it's claimed non-harmfulness!
I thought magnets are meant to be good for your health /alternative lifestyler.