Apple won't have to do that much to comply with EU's new right to repair law
A new EU law means Apple will have to extend its iPhone warranty, and offer all users the same kind of repair or replace service it currently sells as AppleCare.
Since 2020, the EU has been debating right to repair legislation, and it has been steadily progressing through the system. Now the EU has formally adopted the rules, after a vote saw 584 in favor, 3 against, and 14 abstentions.
"Consumers' right to repair products will now become a reality," said EU spokesperson Rene Repasi. "It will be easier and cheaper to repair instead of purchase new, expensive items."
"This is a significant achievement for Parliament and its commitment to empower consumers in the fight against climate change," continued Repasi. "The new legislation extends legal guarantees by 12 months when opting for repair, gives better access to spare parts and ensures easier, cheaper and faster repair."
The EU's statement about the new legislation says that it covers "common household products," and includes smartphones in the list.
Under the new rules, the EU mandates that:
- Warranty guarantees are extended one further year
- Manufacturers must repair devices even after the warranty expires
- Manufacturers must provide spare parts and tools at reasonable cost
- Manufacturers cannot use "contractual clauses, hardware or software" to obstruct repairs
- Independent repair firms must be allowed to use secondhand or 3D-printed parts
- Manufacturers cannot refuse to repair solely for economic reasons
- Manufacturers cannot refuse to repair a device because it was previously repaired by another company
The EU's statement nor the text of the law does not clearly address the issue of parts pairing, where firms make devices fail if spare parts are not bought from the manufacturer. Apple has already allowed used parts in repairs, and there is no scenario where a 3D printed part will need to be activated.
Also, the rules are specifically for consumer devices. There is no detail yet concerning whether anything similar will be required for business-to-business sales of smartphones.
There are further stipulations saying that if an item cannot be repaired, the owner must be offered a replacement. The owner must also be able to borrow a device while repairs are being completed.
Neither Apple's standard warranty nor its AppleCare+ insurance program currently provides a loan device. Under an AppleCare+ plan or initial warranty, Apple already provides a replacement iPhone if a user's one cannot be repaired.
What happens next
Much of the detail regarding these requirements is unclear, such as over what period a manufacturer must continue to offer repairs, how replacements can be offered, or what constitutes "reasonable cost" for parts and tools.
The reason for this is that while the EU has now adopted the legislation, the details will be implemented separately by each of the Union's 27 member states. After a formal approval process by the EU, and official publication, the states will have 24 months to implement the law.
As well as regulatory decisions, the 27 countries and territories will be required to both promote and facilitate the right to repair law. That means information campaigns, repair vouchers, and offering repair courses to the population.
There will also have to be a new EU-wide online platform, divided up into country sections. It will help users find local repair shops, and community-led repair initiatives, such as repair cafes.
Perhaps because of this legislation and its long but steady progress through the EU's parliament, Apple launched its Self Service Repair program in Europe in 2022.
 William Gallagher
William Gallagher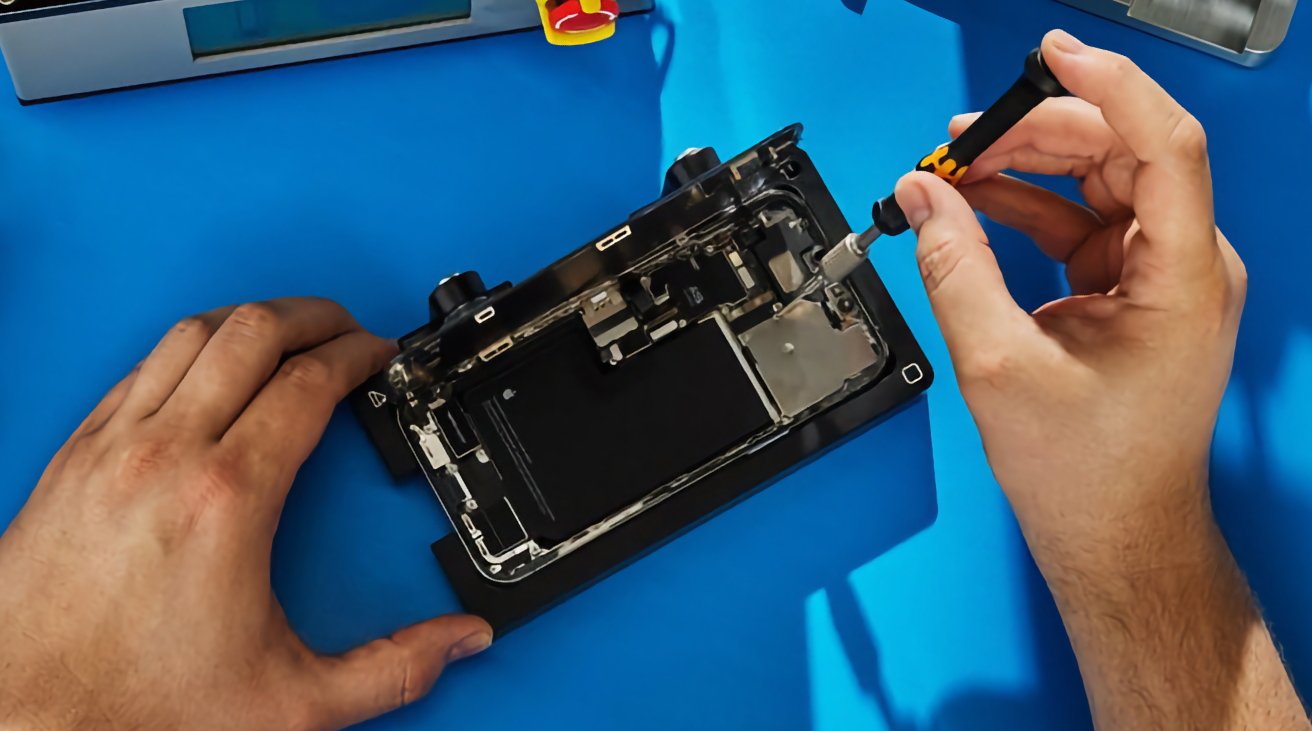












 Charles Martin
Charles Martin

 Andrew Orr
Andrew Orr
 Malcolm Owen
Malcolm Owen
 Christine McKee
Christine McKee
 Chip Loder
Chip Loder









4 Comments
"The EU's statement nor the text of the law does not clearly address the issue of parts pairing, where firms make devices fail if spare parts are not bought from the manufacturer. Apple has already allowed used parts in repairs, and there is no scenario where a 3D printed part will need to be activated."
From 20 June 2025 or from one month after the date of placement on the market, whichever is later, manufacturers,
importers or authorised representatives shall, at least until 7 years after the date of end of placement on the market:
(a) In case the parts to be replaced by spare parts referred to in point 1(a) are serialised parts, provide nondiscriminatory access for professional repairers to any software tools, firmware or similar auxiliary means needed
to ensure the full functionality of those spare parts and of the device in which such spare parts are installed during
and after the replacement;
(b) In case the parts to be replaced by spare parts referred to in point 1(c) are serialised parts, provide nondiscriminatory access for professional repairers and end-users to any software tools, firmware or similar auxiliary
means needed to ensure the full functionality of those spare parts and of the device in which such spare parts are
installed during and after the replacement;
(c) Provide, on a free access website of the manufacturer, importer or authorised representative, a description of the
procedure for the notification and authorisation of the intended replacement of serialised parts by the owner of
the device referred to in point (d); the procedure shall allow for remotely providing the notification and
authorisation;
(d) Before providing access to the software tools, firmware or similar auxiliary means referred to in points (a) and (b),
the manufacturer, importer or authorised representative may only require to have received a notification and authorisation of the intended part replacement by the owner of the device. Such notification and authorisation may also be provided by a professional repairer with the explicit written consent of the owner;
(e) Manufacturers, importers or authorised representatives shall provide access to the software tools, firmware or
similar auxiliary means referred to in points (a) and (b) within 3 working days after having received the request
and, where applicable, the notification and authorisation referred to in point (d);
(f) The access to the software tools, firmware or similar auxiliary means referred to in point (a) may, as regards
professional repairers, be limited to professional repairers registered in accordance with points 2(a) and (b)."
I believe that aspect is covered by the Eco Design legislation...
"Replacement of serialised parts
That is from an older document that I have but I don't have the source link unfortunately so I can't know if it's up to date.