Apple releases iOS 4.3.4 to address PDF security hole
iOS 4.3.4 can be downloaded and installed to any currently supported iOS-based devices by connecting to iTunes and choosing to update. Apple has characterized the latest software as a security update, and does not contain any new features or fixes.
The update is available for the GSM iPhone 4, iPhone 3GS, iPad 2, iPad, and third- and fourth-generation iPod touch. Another firmware, iOS 4.2.9, is also available for the CDMA iPhone 4 for Verizon users.
The update comes just over a week after Apple announced it would release a fix for the security flaw, and less than 10 days after the issue was given widespread attention.
The update plugs a hole that could allow a hacker to utilize a maliciously crafted PDF file to gain access to a user's system. Visiting a site with this exploit could lead to unexpected application termination or arbitrary code execution.
Apple said this is because a buffer overflow exists in FreeType's handling of TrueType fonts, and a signedness issue exists in FreeType's handling of Type 1 fonts.
The update also reportedly contains a patch for iOS's IOMobileFrameBuffer. Apple said the new software addresses an invalid type conversion issue, which could allow malicious code running as the user to gain system privileges.
The PDF exploit became known last week, after hackers utilized it to offer a browser-based "jailbreak" of iOS devices. "Jailbreak" is the term used to describe exploiting flaws in iOS code to allow users to run software that is not approved by Apple.
While those behind the jailbreakme.com site did not create it with malicious intent, it's possible that a more nefarious hacker could release an exploit that, when visited by a user, could allow unsigned code to be run on an iPhone or iPad without the user's permission or even knowledge.
 AppleInsider Staff
AppleInsider Staff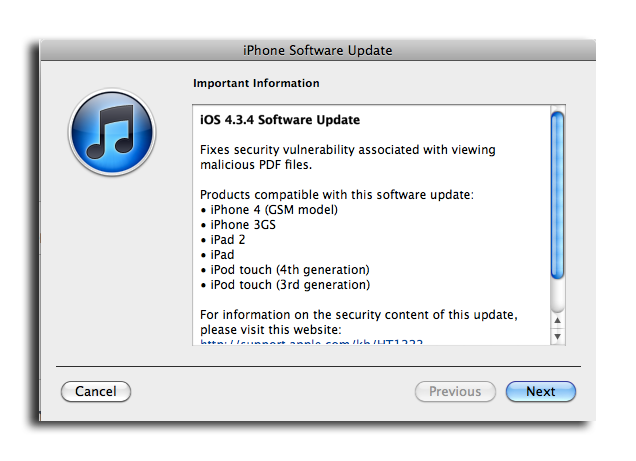






 Amber Neely
Amber Neely
 Thomas Sibilly
Thomas Sibilly
 William Gallagher
William Gallagher
 Malcolm Owen
Malcolm Owen
 Christine McKee
Christine McKee









60 Comments
Edit: nevermind they have an update for CDMA users too. I'm gonna download it real quick
Thank God one of the advertised "features" of the Google phones is that you can root them!
Wait a minute. If you can root them, can't somebody else, for less "it's my phone!' motives? Or, wait, somebody sending you a malicious pdf can make it HIS phone.
It's always seemed a strange, quixotic belief, those who buy phones to jailbreak them.
Looks like your still SOL if you have the CDMA version....
No, there is an update 4.2.9 for CDMA phones.
Thank God one of the advertised "features" of the Google phones is that you can root them!
Wait a minute. If you can root them, can't somebody else, for less "it's my phone!' motives? Or, wait, somebody sending you a malicious pdf can make it HIS phone.
It's always seemed a strange, quixotic belief, those who buy phones to jailbreak them.
Well there's a difference between OS supported rooting that requires an explicit user approval and a hacked rooting that just requires downloading a PDF. The former is a feature, the latter is most definitely a bug.
Well I am sure a few million people, myself included, took advantage of this easy method to update the version number of our software and keep our phones jail broken and unlocked.