Perhaps reflecting a desire to maximize power efficiency in all areas, a newly-published Apple patent application showcases a "hybrid" display mixing OLED and quantum-dot LEDs.
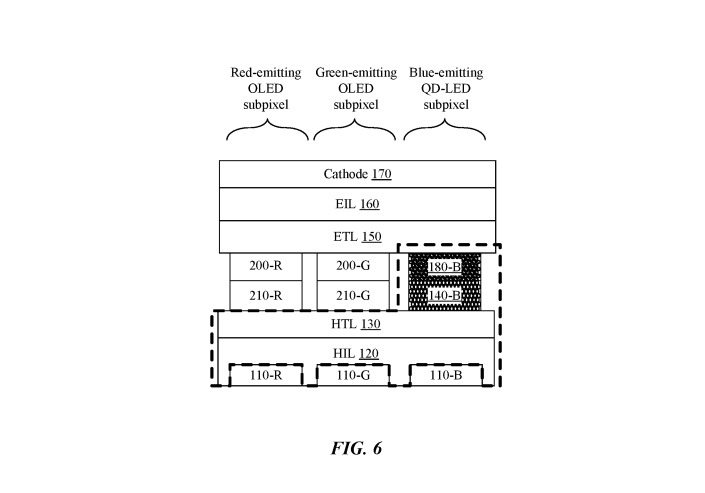
The U.S. filing, no. 20,190,131,356, describes a "tandem hybrid pixel" with an OLED subpixel and a quantum dot subpixel, plus various needed transport layers and cathodes.
Quantum Dots are photoluminescent particles included in an LED-backed TFT display that can produce brighter and more vibrant colors, with the colors produced depending on their size. While available in current QLED televisions, the technology is only really being used to enhance the backlight, rather than being used to illuminate individual pixels.
The technology in theory can create an even thinner display than OLED, along with a more streamlined manufacturing process. True QD displays are also capable of high pixel densities of up to 1,000ppi, multiple times the density required to be called a Retina-quality display, and based on Apple's hybrid invention, will also boost the response times of OLED technology.
Apple's latest submission notes that while OLED on its own offers advantages like fast response and power effiency, quantum-dot LEDs (QD-LEDs) are potentially even more efficient.
Apple's latest patent on the subject was originally submitted in December 2018, and credits several inventors, all of them based in California at the time.
The most significant though may be Jonathan Steckel, formerly responsible for quantum dot work at QD Vision before he joined Apple in 2014 as a "Lead Technologist in Emerging Display Technology Development." That subtitle switched in January 2019, with him moving to facilities in Grenoble, France to oversee "Camera Core Tech & Display Engineering."
A previous version of the application was published in August 2017. Apple has also filed for several other patents related to quantum dots, covering concepts like MEMS shutter control and backlight dimming.
The three most power-hungry components in a mobile device are typically the display, the main processor, and wireless chips. Reducing energy consumption may be especially critical as Apple moves deeper into the wearables market.
Beyond the Apple Watch, the company is believed to be working on an augmented reality headset that could ship as soon as 2020. First-generation hardware may be dependent on a paired iPhone for most processing, but the company will likely need high-efficiency eyepieces to ensure all-day battery life.
Another display technology on the horizon is microLED — Foxconn is reportedly amping up development to secure orders from Apple for future iPhones. MicroLED panels are their own backlight, once again improving efficiency. Other advantages over OLED include brighter images and less susceptibility to failure. It will take some time, however, before manufacturing becomes economical for mass production.
 Roger Fingas
Roger Fingas






-m.jpg)





 William Gallagher
William Gallagher
 Amber Neely
Amber Neely
 Andrew Orr
Andrew Orr
 Wesley Hilliard
Wesley Hilliard

 Oliver Haslam
Oliver Haslam
 Christine McKee
Christine McKee







8 Comments
Apple is constantly getting sued by every swinging schwanzstucker with some kind of patent they own. Apple tech blogs constantly report patents applied for by Apple. When has Apple EVER sued somebody for patent infringement (other than the Samsung “design” lawsuit)? Who has Apple sued for a real tech patent and does Apple have any FRAND related patents it licenses? Are Apple patents just smoke and mirrors? Is Apple really just a design company that refines and fine tunes other’s work? I’m beginning to wonder.
this is incredible, I remember when it took forever to for monitors to receive any update. now I can barely enjoy my phone long enough before coveting the next one.
OK that is equivalent to admitting that the OLED has no future, at least without Quantum Dot. Red and Green subpixels are OLED, the Blue subpixel is Quantum Dot. What I understand from that it is the Blue OLED that fails first. As stated in the patent "
http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO2&Sect2=HITOFF&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsearch-adv.html&r=1&p=1&f=G&l=50&d=PG01&S1=10192932&OS=10192932&RS=10192932
CES this past year saw an interesting development in TV's. I forget what company did it, but it was a novel approach to getting OLED like blacks from a LED TV. Also it wasn't in a shipping product, just a tech demo.
Anyway, they had a bright white full array LED backlight, with many local zones for dimming. Then on top of that, they put a basic TFT screen that only did black and white (or, in this case, opaque and transparent). Then the top layer was the color layer. So in addition to the local dimming backlight, the TFT screen also would activate and block additional light from bleeding. The end result was OLED like contrast using just LED tech.
Pretty neat. Don't know how it would work on smaller displays like phones and watches, but for TV's it was a great step forward using cheaper panels then what a full OLED would cost. I believe it was pretty thick though thanks to all the layers, but again it was a tech demo, so that's a problem that can be solved. Also thickness isn't as big a deal in the TV world.
Curious as to why Apple is working on displays when they currently buy them in from third parties?