The main selling point of the iPhone 12 is 5G wireless connectivity, but there are many aspects to that network. Here's how to figure which network you're connected to, whether it's sub-6GHz, mmWave — or something else.
The iPhone 12 is Apple's first 5G-compatible smartphone. As 5G expands across the globe, iPhone users will be able to access the next-generation standard for broadband cellular networks.
In order to find out what 5G connection you're connected to, you just have to look to the carrier network badge.
In the top right corner of your iPhone 12, you'll find a small icon — if you're currently connected to Wi-Fi, you'll see the Wi-Fi symbol. However, in the event that you're not connected to a router, you'll see your carrier's network badge instead.
If you see just the "5G" symbol, that means you're connected to standard 5G, on the sub-6GHz spectrum. This spectrum can be faster than LTE but slower than mmWave and higher-frequency 5G bands. We've discussed these differences in the past.
If you see a "5G UW" with a Verizon phone or "5G+" on an iPhone connecting to AT&T's network, that means you're connected to the carrier's higher-frequency mmWave version of 5G. These bands are faster than standard 5G — but that speed comes at the cost of having a reduced range.
If you see a "5G E" symbol, you are not connected to a 5G network. The 5G E label indicates AT&T's "5G Evolution" network, which was misleadingly applied to its next-generation LTE network. As we've pointed out in the past, tests have shown that 5G E is only a hair faster than AT&T's LTE, but all other things the same, notably slower than Verizon and T-Mobile's LTE networks.
Of course, 5G isn't ubiquitous yet, and chances are you'll probably find that you're still connected to LTE in some situations — and your phone will indicate LTE for most, and possibly 5G E for AT&T customers. This may be because you're in an area where 5G hasn't rolled out yet — especially true for rural areas.
The iPhone 12 also provides a service called "Smart Data mode." This mode, which is activated by default, will only activate 5G under certain conditions, such as when you need the extra speed and you've got the data to spare. It also saves on battery life.
In some cases your iPhone may show that you can connect to 5G, but may actually drop your connection to LTE to save on data and battery life. In these instances, your iPhone will display the 5G badge but will be connected to LTE instead.
Of course, if you'd prefer to switch 5G permanently on or off, there's a toggle available in your iPhone's Settings app under Cellular Data Options.
 Amber Neely
Amber Neely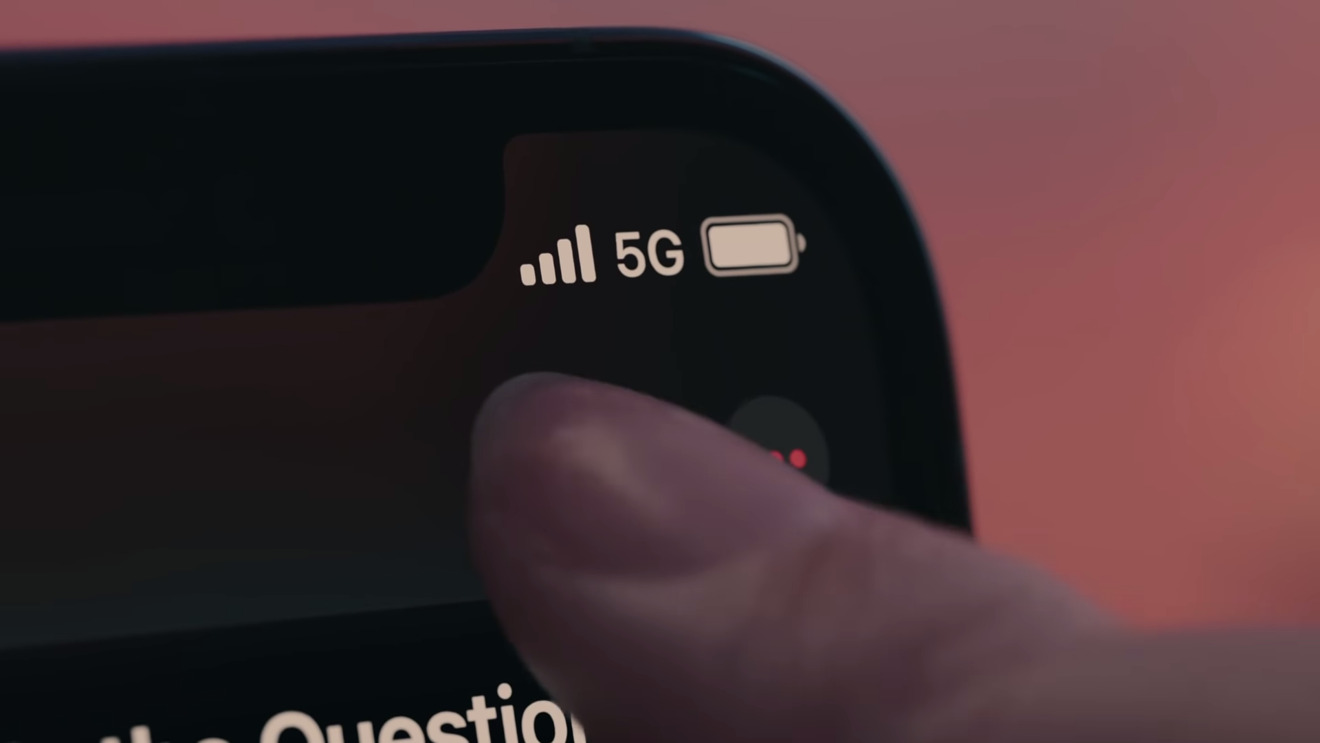









 Christine McKee
Christine McKee
 Andrew O'Hara
Andrew O'Hara
 Malcolm Owen
Malcolm Owen

 William Gallagher
William Gallagher