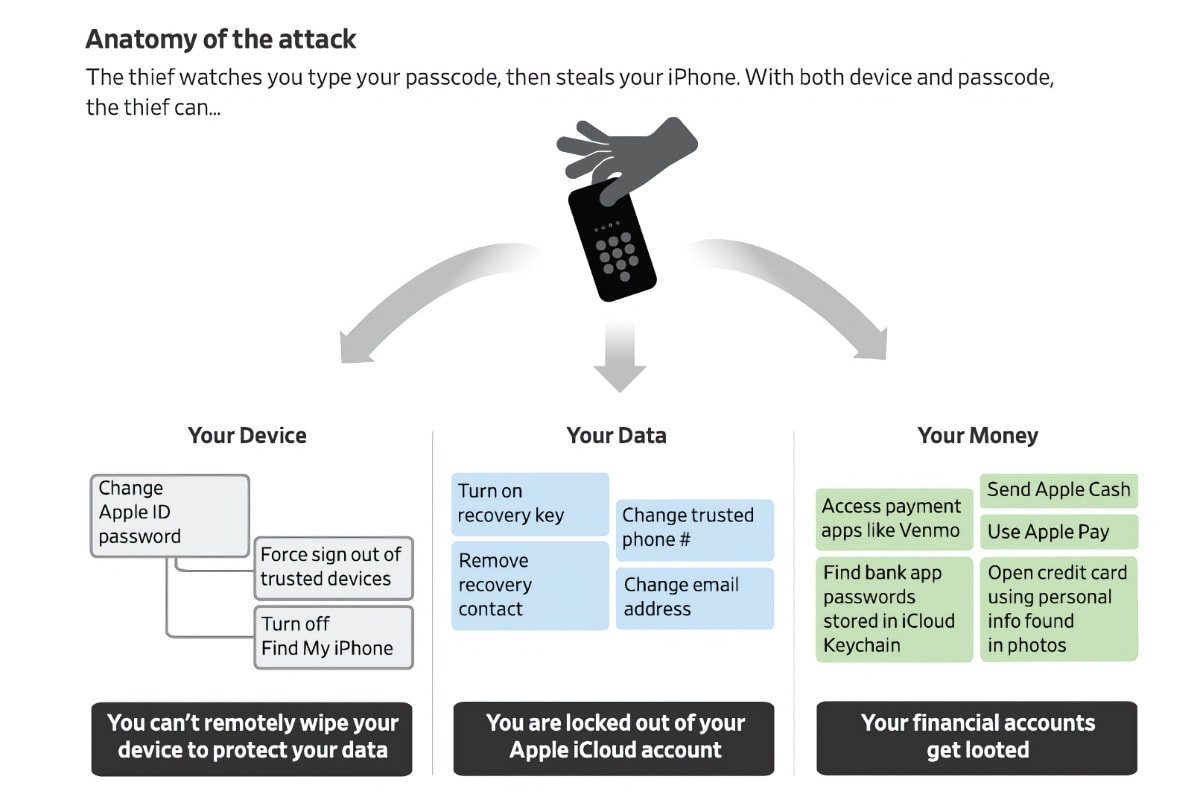
A new report highlights that when a thief has both an iPhone and the corresponding passcode, a user's entire digital life is at risk. While this is in no way new, there are some simple steps to mitigate the risk.
The "hack" involves the thief watching the victim type in their passcode, then steal the iPhone to access their data. In one case, a victim was locked out of her Apple account and lost about $10,000 from her bank account, according to The Wall Street Journal.
Because the login passcode offers access to most other apps — and system settings — a thief can use it to change the Apple ID password to lock victims out. "Once you get into the phone, it's like a treasure box," said Alex Argiro, who investigated a high-profile theft ring as a New York Police Department detective before retiring last fall.
The thief can also use the device passcode to access iCloud Keychain, which puts a person's entire online life at risk. Argiro said these opportunistic crimes have increased in the past two years in New York. "This is growing," he said. "It is such an opportunistic crime. Everyone has financial apps."
All victims The Wall Street Journal interviewed had their iPhones stolen while socializing in public in places like bars. In some cases, victims were physically assaulted and intimidated into handing over their phones and passcodes, and others believed they were drugged.
Sgt. Robert Illetschko, the lead investigator in one case, said groups of two or three thieves would go to a bar and befriend the victims to try and access their iPhones. If they couldn't watch the victim type in their passcode, the thieves might try to get them to open a social media app or have the victim hand over their phone for a picture.
Similar cases have been reported in Austin, Denver, Boston, and London.
In another case, a man had his identity stolen because he had saved photos of his passport, driver's license, paycheck direct-deposit form and health insurance paperwork in the Photos app. He was able to regain access to his Apple ID, but it's highly likely the thief kept the sensitive information.
Face ID or Touch ID can help prevent such attacks since people won't need to type in a passcode. But in New York, authorities have suggested Face ID as a possible entry point into iPhones.
Similar to a passcode, a thief could grab an iPhone after a victim logs in using biometrics, then prevent the iPhone from going into sleep mode. However, that access would be more limited since a passcode is needed to enter Face ID or Touch ID settings.
Apple users can turn on a feature called Attention Detection for Face ID in Settings > Face ID & Passcode. It requires a person to look at the iPhone before it authenticates the log in, meaning thieves who drug their victims can't log into the iPhone with this method.
As The Wall Street Journal noted, iOS doesn't require a person to enter an older password before setting a new one for Apple ID. Hardware security keys supported by iOS 16.3 didn't prevent account changes using only the passcode.
The passcode could even be used to remove security keys from the account.
An Apple spokeswoman did say that account recovery policies are in place to protect users from bad actors accessing their accounts.
"We sympathize with users who have had this experience and we take all attacks on our users very seriously, no matter how rare," she said, adding that Apple believes these crimes are uncommon because they require the theft of the device and the passcode. "We will continue to advance the protections to help keep user accounts secure."
Apple generally doesn't allow users to regain access to a stolen account, if a thief sets a recovery key on the Apple ID that the victim can't access.
How to protect yourself
It's not certain why the Wall Street Journal is treated this like a new emergency, or an emergent vector of attack. Passcode theft has always been at some level a concern for users, and it has always been good advice to secure that code.
In some of the cases, thieves were able to steal a victim's Social Security Number because of tax forms saved in iCloud Photos. Some Apple apps let users search for text, and searching for "SSN" or "TIN" (taxpayer identification number) in Apple Photos produced the document photo.
Although iCloud encryption can help prevent online hacking, it can't stop thieves from accessing sensitive information once they have iPhone access. So, storing such information in Apple Notes, Photos, or other apps is dangerous.
Next, Apple users should set their own Apple ID recovery key, which prevents anyone else from doing it.
- On an iPhone or Mac, go to Settings > Your Name > Password & Security.
- Tap Recovery Key, then slide to enable it. On a Mac, click Manage next to Account Recovery.
- Tap Use Recovery Key and enter the device passcode.
- Write it down and store it in a safe place, then confirm it on the next screen.
People should also set up Attention Detection for Face ID in Settings > Face ID & Passcode. This will prevent the theoretical attack against being drugged and unlocking the phone with Face ID.
Perhaps there is more the company could do to prevent such crimes. But, in the meantime, as it has always been, Apple users should be wary of typing their passcodes in public or handing their device to a stranger.
 Andrew Orr
Andrew Orr






-m.jpg)






 Bon Adamson
Bon Adamson
 Marko Zivkovic
Marko Zivkovic
 Wesley Hilliard
Wesley Hilliard
 Amber Neely
Amber Neely

 Malcolm Owen
Malcolm Owen
 William Gallagher
William Gallagher




-m.jpg)



35 Comments
I use another phone that has no financial apps on it. I take this out into the community. On my Apple Watch I deleted all financial apps. I use these at home on my iPhone
Good article. Freaky situation. Time to tighten up my iPhone.
An iPhone problem? Android phones never are stolen?
Diversifying limits risks.